Understand Hepatitis[3]
Hepatitis is the term used to describe the inflammation of the liver, caused by a viral infection or liver damage. There are five types of viral Hepatitis:
- Hepatitis A is most commonly transmitted by consuming food or water contaminated by faeces from an infected person.
- Hepatitis B is transmitted through contact with infectious body fluids, unsafe sex or sharing razors etc. with an infected person.
- Hepatitis C is transmitted through direct contact with infected body fluids, typically through injection drug use and sexual contact.
- Hepatitis D is a rare form of Hepatitis that only occurs in conjunction with Hepatitis B infection.
- Hepatitis E is a waterborne disease caused by the Hepatitis E virus (HEV).
Symptoms
Most people experience mild or no symptoms.[4] The incubation period for different Hepatitis types varies as follows:
- Hepatitis A: 14 to 28 days[4]
- Hepatitis B: 75 days on average, but can vary from 30 to 180 days [5]
- Hepatitis C: 2 weeks to 6 months[6]
- Hepatitis D: Approximately 35 days[7]
- Hepatitis E: 2 to 10 weeks, with an average of 5 to 6 weeks[8]
The initial phase of Hepatitis is called the acute phase. The symptoms include:[9]

Fever

Jaundice

Muscle Pain

Dark Urine

Joint Pain

Loss of Appetite

Fatigue
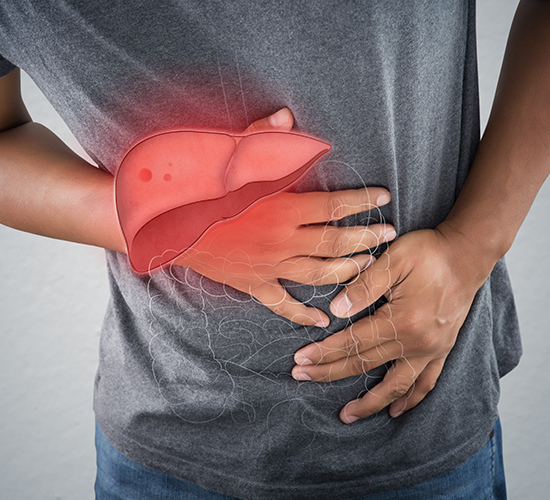
Abdominal Pain
The acute phase is not usually dangerous, but in certain cases, it can result in acute liver failure and death. It could also progress to a chronic infection. This is most likely with Hepatitis B and C viruses. As the disease progresses, chronic Hepatitis can lead to:

Liver Failure

Itching

Swelling of the lower extremities

Confusion

Blood in the faeces or vomit
Diagnosis[10]
Most new infections with the Hepatitis viruses are asymptomatic or undiagnosed. Due to its largely asymptomatic nature, viral Hepatitis is a silent epidemic; most people are unaware of their infection.
A number of blood tests are available to diagnose people with Hepatitis, which can be used to distinguish acute and chronic infections. Diagnosis of Hepatitis infection can be done through serological tests to detect antibodies specific to the type of infection. Test to detect viral RNA and DNA can help in diagnosing active infections and improve outcomes in viral Hepatitis. Its benefits are:[11]
- Shorter Treatment Period: Even patients with heavy viral loads of Hepatitis can be cured a few weeks earlier compared to the standard duration of antiviral therapy.
- Lower Risk of Complications: Undetected and untreated chronic Hepatitis can lead to complications such as liver cirrhosis. Hepatitis treatment is most successful in stopping the deterioration of the liver if it is started before the deterioration begins.
- Reduced Risk of Liver Cancer: Chronic Hepatitis is a risk factor for primary liver cancer. Treating it early can significantly reduce the chances of cancer.
- Lower Risk of Transmission: Even patients with low viral load can transmit the virus to others. Starting treatment early can help eliminate the virus more quickly and prevent its transmission.
Prevention[12]
Prevention is the most effective approach against the disease. Prevention of Hepatitis requires improvements in sanitation, food safety, immunization, blood safety and reducing the risk of exposure to the virus in health-care settings and in higher risk populations.
The spread of Hepatitis can be reduced by:
- Vaccination programmes
- Adequate supplies of safe drinking water and proper disposal of sewage
- Personal hygiene practices such as regular hand-washing before meals and after going to the bathroom
- Safe and appropriate use of health care injections and safe handling and disposal of sharps and waste
- Provision of comprehensive harm-reduction services to people who inject drugs including sterile injecting equipment and effective treatment of dependence
- Testing of donated blood
- Training of health personnel
- Practicing safe sex
- Hand hygiene in surgical hand preparation, hand washing and use of gloves
Screening Of Donated Blood[13]
Hepatitis screening involves testing of donated blood for antigens and/or antibodies to determine whether the donated blood has presence of viral Hepatitis. Advance screening involves testing for viral DNA or RNA in blood. Globally, however, there are significant variations in the extent to which donated blood is screened. As a result, in many countries, the recipients of blood and blood products remain at an unacceptable risk of acquiring life-threatening infections.
In India, according to the requirements of The Drugs and Cosmetics Act 1940[14], it is mandatory to screen every unit of blood for HBV and HCV (alongside with HIV, syphilis, and malaria) before transfusion, in all licensed blood banks. Screening for Hepatitis C was introduced in 2001[14] and made mandatory across blood banks in India.
Hepatitis can progress to jaundice
Only chronic hepatitis can cause liver cancer
In India, every unit of blood is screened for HBV and HCV
References
1. https://www.worldhepatitisalliance.org/world-hepatitis-day-2019
2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4298630/
3. https://www.healthline.com/health/hepatitis#types
4. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-a
5. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b
6. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c
8. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-e
9. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hepatitis-a/symptoms-causes/syc-20367007
10. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5389598/
11. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5389598
12. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4245-hepatitis-viral-hepatitis-a-b–c/prevention
13. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92029/
14. http://www.naco.gov.in/sites/default/files/Drug%20%26%20Cosmetic%20Act%201940_1.pdf